Python 04
Python Functions 03
Lamda - anonymous function
Lambda is a function that has no name. It makes the function a one-liner function.
def sum(a, b):
return a + b
sum2 = lambda a, b: a + b
Implicit return
From the above function, you can see there is no return state for the lambda function. Implicit return means the function returns the value without the return.
The basic Lambda function structure will be like this:
# structure
lambda arg1, arg2: <exp>
# example
greet = lambda greet, name: f'{greet}!! {name}!'
print(greet('Chao', 'Panda'))
Unit tests
Testing your code before launching the app will be important when you enter the production level. In this part, we will not go too deep but will learn how to check our written code can be tested.
def sum(a, b):
return a + b
def test_sum():
assert sum(1, 5) == 6, '✅ test passed'
assert sum(-10, 10) == 5, '❌ sum does not return correct result'
assert sum(20, 20) == 1000 , '❌ sum does not return correct result'
assert sum(250, 480) == 730, '✅ test passed'
print('✅✅ ALL Test passed(4/4) !!')
test_sum()
Imagine we are testing the sum function. You can test the function with assert. The basic structure is simple.
- Put assert in front of the function.
- Check the result with
==
assert sum(1, 5) == 6
- And put a comma and comment if the result is correct. (or not correct)
print("your_msg")is optional.
assert sum(1, 5) == 6, '✅ test passed'
assert sum(-10, 10) == 5, '❌ sum does not return correct result'
print('✅✅ Test passed(2/2)')
Exercise
Try to assert calculateFoodTotal() that we created earlier.
def calculateFoodTotal(food: float, tip_percentage: int) -> float :
tip = food * (tip_percentage / 100)
total = food + tip
print('\n\n')
print('=================================')
print(f'🍗 Food Amount: ${food}')
print(f'💸 Tip Amount: ${tip}')
print('\n')
print(f'💰 Total Amount: ${total}')
print('=================================')
return total
calculateFoodTotal(food, tip_percentage)
Try to write test cases you would like and see the results.
Toggle Answer 👇
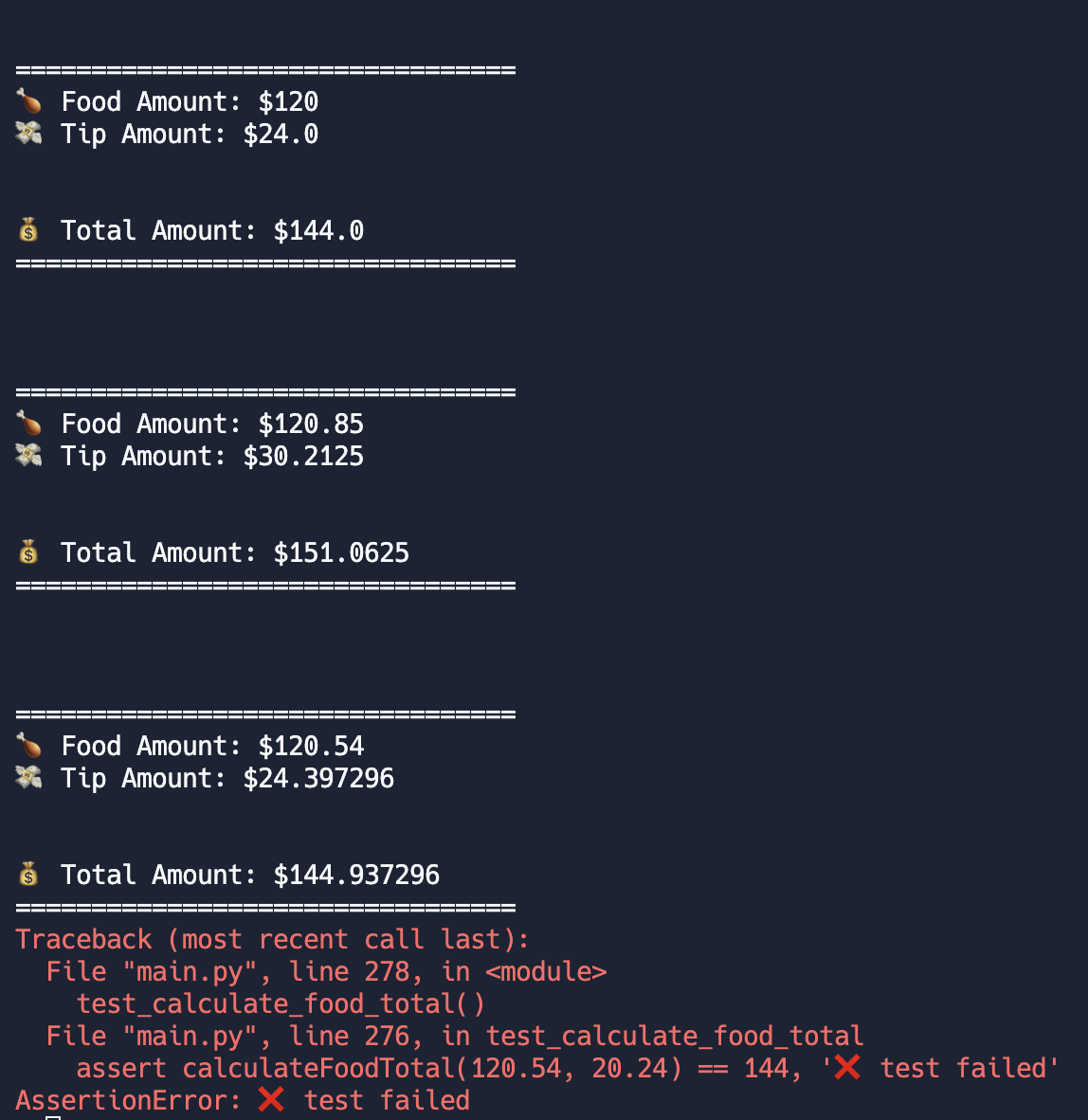
def test_calculate_food_total():
assert calculateFoodTotal(120, 20) == 144, '✅ test passed'
assert calculateFoodTotal(120.85, 25) == 151.0625, '✅ test passed'
assert calculateFoodTotal(120.54, 20.24) == 144, '❌ test failed'
test_calculate_food_total()
While statement
Now, let’s talk about the while statement.
distance = 0
while distance < 20:
print(f"I'm running {distance}km")
❗ Don’t run this code from your terminal ❗
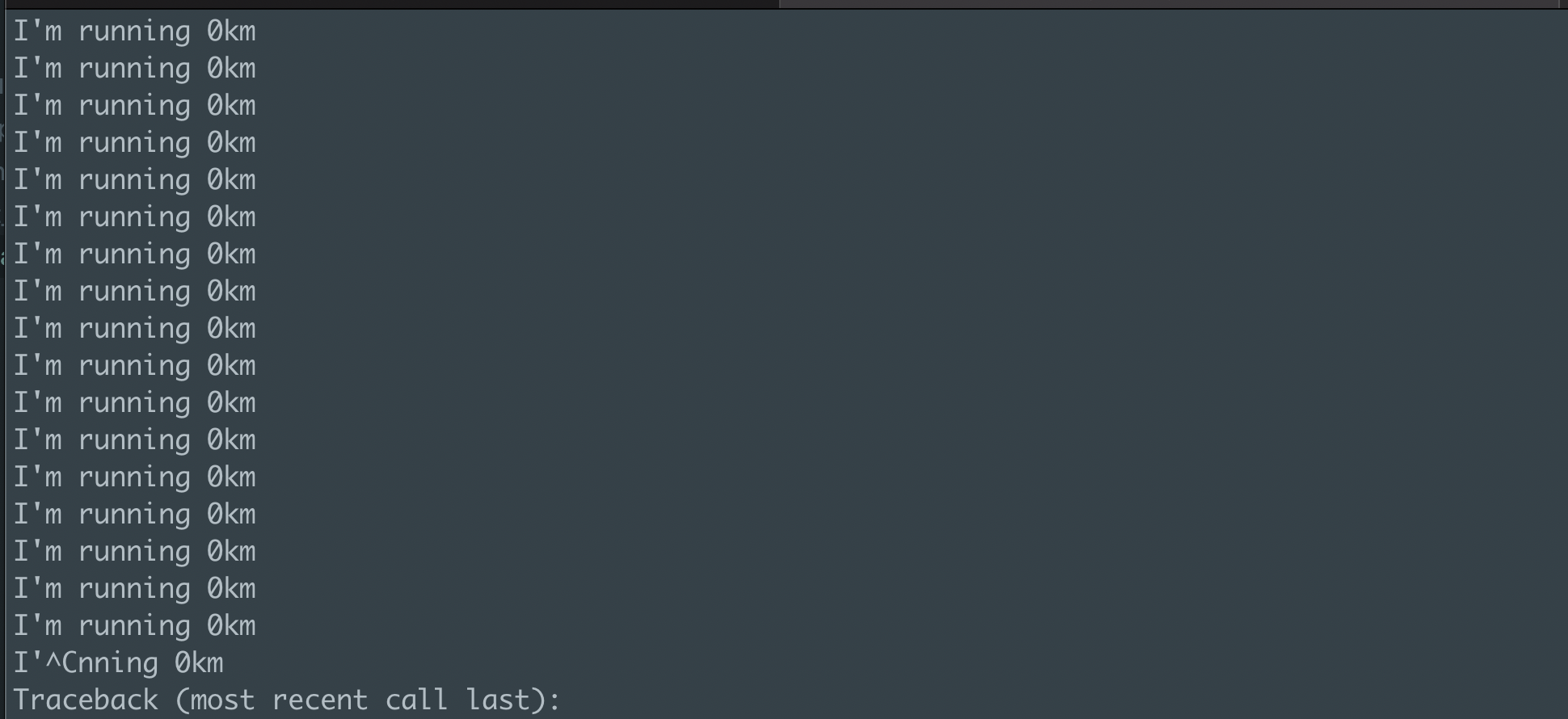
It will run the code endlessly because the condition is true.
If you already ran this code, please do
Ctrl + Cfrom your terminal.
How to fix this problem? Try to run the code below.
distance = 0
while distance <= 20:
print(f"I'm running {distance}km")
distance += 1 # same as distance = distance + 1
Number Guessing Game
As we learned while, why not use it?
We are creating a tiny game app with while, which will help us understand it better.
print("Welcome to Number guessing game")
winning_number = randint(1, 50)
You need to know the Python standard library to create a random number.
Python Standard Library
Python has its own library, and we used it already. When? We have been used print(), input(), and int().
Check out the Python standard library here
Because of the size of the library, python can’t always load the whole library. So, to use randint(), we need to import it from the standard library.
from random import randint
This is how we can bring functions from modules.
Now we can use randint(), and continue to make the game.
from random import randint
print("Welcome to Number guessing game")
winning_number = randint(1, 50)
playing = True
while playing:
user_number = int(input("What is your number? : "))
if user_number == winning_number:
print("Congrats!! You win!")
playing = False
elif user_number > winning_number:
print("Sorry, Go lower")
elif user_number < winning_number:
print("Sorry, Go higher")
The result should be like this:
Click Me

❗Remember, while runs the code if it is true. Stopping the while function will be the developer’s duty. Check and try to understand the control flow of the game, not just memorize it.

Comments