[Frontend] TIL Frontend project - HTML/CSS, JavaScript

FASTCAMPUS Frontend Project
Learning HTML/CSS, JavaScript
패스트캠퍼스 - 프론트엔드 웹 개발의 모든 것 초격차 패키지 Online 과정
🧩 What I Should Learn?
- What is a Frontend development
- How does the Web Application work?
- Web Standard
- Web Images
- Open-source License
🎯 What I learned today
The Front-end Development
Definition of front-end development
Front-end web development is the developement of the GUI(graphical user interface) of a website through the use of HTML, CSS and JavaScript. Users can view and interac with that website by front-end development. - Wikipedia
If I explain front-end development, the browser has the back-end and the front-end structure, whereas the back-end handles the complicated business logic or the important data. While the front-end mainly focus on the user interface including UX/UI, and by the front-end development, the application is possible to deal with the user(customers) for the company’s service/website.
Front-end basic structure
HTML
Abbreviation for HyperText Markup Language. HTML is the standard markup langauge for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser.
HyperText in simple term is when we click hyperlink, it takes us to the different page. Think as this Link is hypertext and the language can create or markup those feature is HTML.
Deal with the web structure and elements like Page, Title, Paragraph, Table, Image and Video.
CSS
Abbreviation for Cascading Style Sheets. CSS is a style sheet language used for decribing the presentation of a document written in a markup language.
CSS is the part for styling or printing ingridients on actual screen. It handles the Font, Color, Size and Layout, and other visual aspects of a website(mainly static content).
JavaScript
JavaScript in simple term is a programming language that enables dynamic content on websites. It often used for creating interactive and responsive user interfaces.
Wrap up

Let’s imagine we create the emoji above.
The HTML will be the structure of the emoji, like the components of the emoji. It will declare the emoji has two eyes, mouth and face, but doesn’t know where to put it. It exist as the skeleton.
The CSS will form the emoji face. It colors the face in yellow, face to be circle and the smile. It works as a designer or the skin of the emoji.
The JavaScript will make the emoji actually move. If we can control the emoji, JS will handle that ability too. It changes the content from static to dynamic, and brings the structure and skin to life.
Web Application
How does Web Application work?
The web application is working on the browser. When we go to the browser like Google Chrome, Safari or Firefox, we initially type the address with the http protocol. Typing the address and hit enter, the browser send a request to somewhere.
https:// (this is a http protocol) + //your address goes here.com
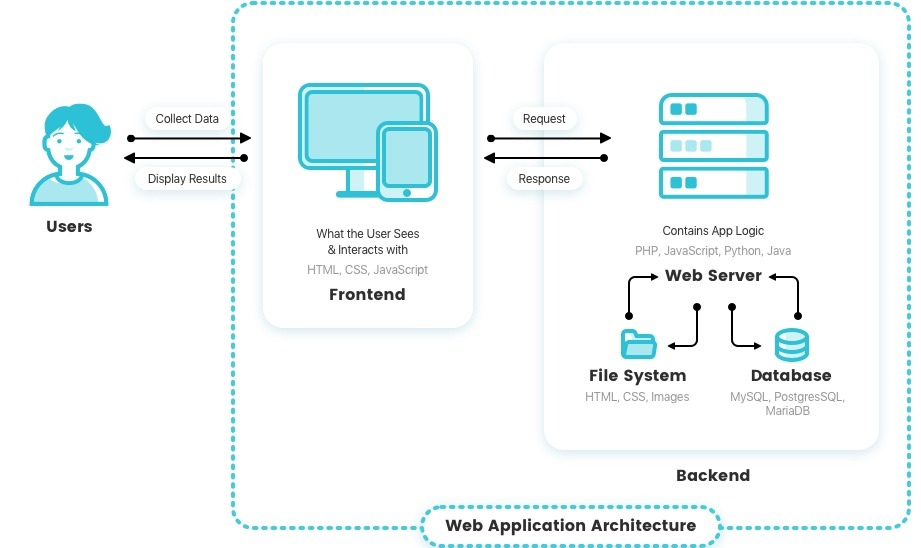
In technical term, we call this process as a request. The request from the browser go to the server(backend), and the server returns the response.
The browser get the response and render the page with HTML, CSS and JavaScript. If the user interact with the rendered components on the website, the browser repeating above step.
When the user want to go to different page or interact with the UI, the browser send additional request, and the server replies with the adequate response.
Local development
To develop the web page above, we need an environment for the developers. As we need a computer to develop the application, we call this developer computer a local development environment.
On the other hand, when the developer finish to develop locally, the application only work in their machine. In order to deliver the application to the users, the developer have to upload the application on the server.
Then the developer will set the address for the application, thereafter the user can access the application with the address.
Web Standards and Browser
Web standards
Web standards are technologies used to build websites. It refers to a set of guidelines, specifications, and best practices established by W3C(World Wide Web Consortium).
The standardization organization W3C, has several levels when they set the recommendations.
- Working Draft (WD)
- Candidate Recommendation (CR)
- Proposed Recommendation (PR)
- W3C Recommendation (REC)
And the REC level is set to the web standards, which includes the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
If you want to learn more on Web standards maturity levels, click here
Browser
Browsers like Chorme or Firefox are coming from the browser vendors such as Google, Micorsoft, Mozilla or Apple.
The browser vendors interpret this web standards in their own way, and implement interpretation to their browser.

Cross browser compability
Cross-browser compability can be defined as the ability of a web application or script to support various browsers indentically.
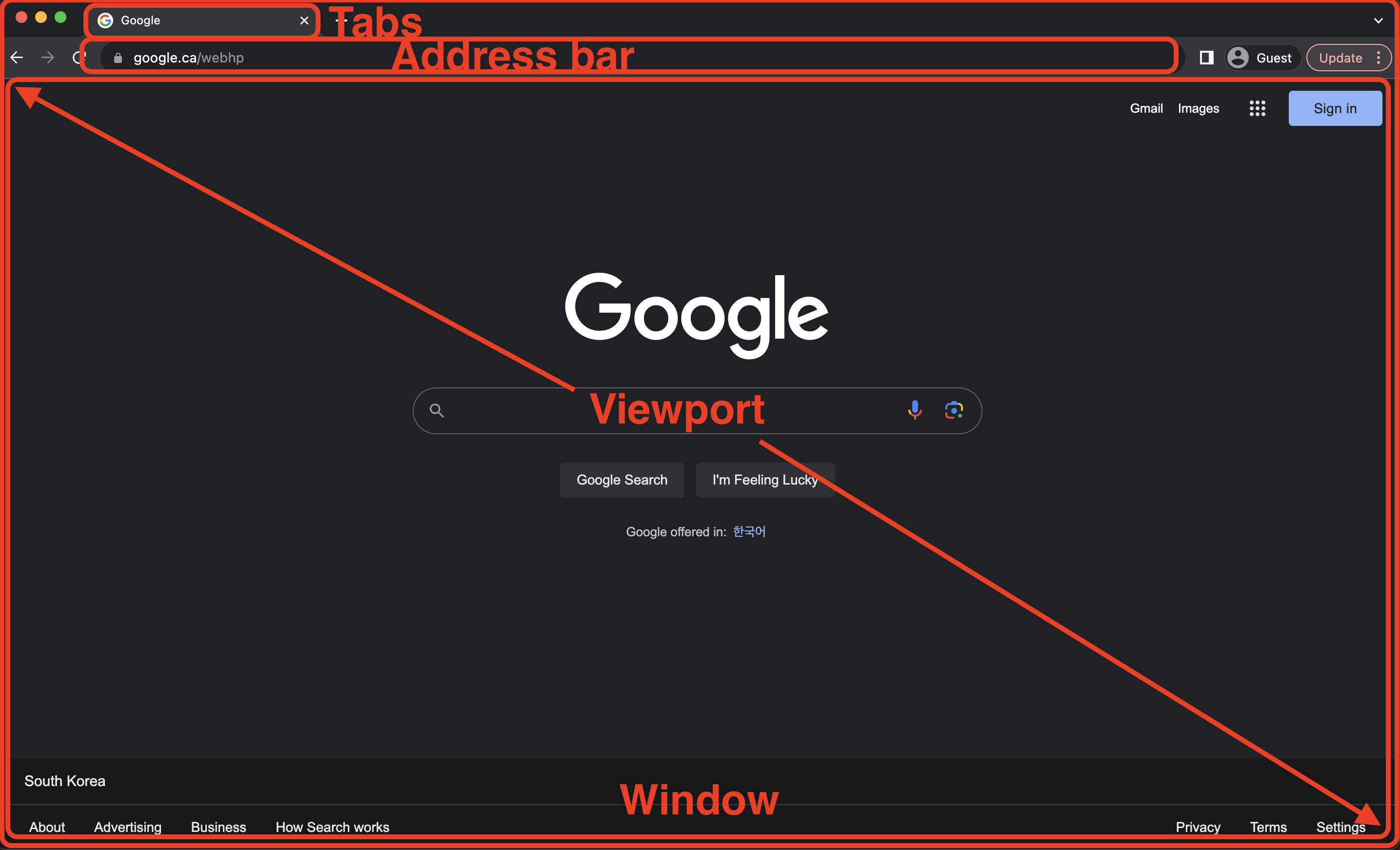
Browser Interface
To briefly go over the browser interface, the browser has a window, tabs, address bar and viewport.
We don’t have to care about the details but remember the viewport is the area that renders a webpage.
Web Image
Bitmap
Bitmap or raster images are made up of pixels, where each pixel contains a color information.
Bitmap images are resolution dependent, hence enlarging an image can result in a loss of quality and pixelation. Bitmap images are designed for complex details and suitable for photography or complex graphics.
JPG
JPG or JPEG stands for the Joint Photographic Expert Group, is commonly used method of lossy compression for digital images.
The degree of compression can be adjusted, that allows users to choose between the image quality and storage size.
PNG
PNG stands for Portable Network Graphics, is a raster graphics file format that supports lossless data compression. However, lossless compression typically leads to a larger file size.
PNG supports transparency including alpha channel(partial transparency), and this is the key difference compare to JPG.
GIF
GIF stands for Graphics Interchange Format, is known for its ability to support animations. It uses a lossless compression to preserve the image quality.
GIF uses 8 bits, which pallete up to 256 colors, hence it has a limited color depth. It is suitable for basic web animations and memes.
WEBP
WEBP is a modern image format developed by Google that provides both loss and lossless compression for images on the web.
Similar to GIF, WebP supports transparency and animation, and also known for its efficeint compression algorithms that provide high image quality at smaller file size.
While support has grown, it has been in the market a little over ten years. Thus, not all browsers support webp, especially older browser like IE, may not support webp.
Backward compatibility
Backward compatibility refers to the ability of software, hardware or technology to maintain a high degree of interoperability between modern and legacy systems.
For instance, to use webp, developers should check the backward compatibility.
Vector
Vector images are base on mathematical equations to represent shapes. It made up of lines, curves or points.
Vector images are resolution independent, and they can be scaled to any size without loss of quality. These images are ideal for logos and icons that need to be displayed consistently across various devices.
SVG
SVG stands for Scalable Vector Graphics, is an XML-based vector image format designed for the web.
SVG images are resolution independent, which makes them ideal to the responsive web design.
Mainly, SVG supports interactivity and animation using CSS and JavaScript which means the developer can control them with code.
Open Source License
Definition of Open-source license
Open source licenses are designed to promote the sharing of software, encourage collaboration, and allow users to freely use, modify, and distribute the source code.
While developing the application, we often go to the internet and search for the source code. But keep in mind that the source code also has a copyleft.
Hence we have to check the copyleft policy before we use any open source code from the internet.
The famous common open licenses are like the ones below:
- MIT License
- Apache License
- BSD(Berkeley Software Distribution) License
- MPL (Mozilla Public License)
- Beerware
Again, there are no such free sources and the open-source has the copyleft, which is a general license agreement granted by a copyright owner permitting anyone to freely use copyrighted property but under specific terms.
📌 Takeaway
- Front-end development is a development for GUI that allows users to interact with the website.
- The browser work in three step. When user type the address, the browser sends the
requestwith http protocols. The server gets the request and returns theresponse. When the browser get the response, the browserrenderthe page. - Web standards are the guidlines and best practicies estalished by W3C, including technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Web images has various formats mainly divided to bitmap(raster) image and vector image.
- Choosing right image format for each purpose is the main key for the front-end developer.
- Open-source licenses often has a copyleft which allows the developers to freely use under certain conditions.
💻 Solution
- None
🔖 Review
- HTML is skeleton, CSS is a skin, and JavaScript is like digestive and respiratory systems that brings the structure and skin to life.
- Bitmap(raster) image formats are JPG, JPEG, PNG, GIF and WEBP.
- Vector image format is SVG and it is suitable for responsive design.

Comments